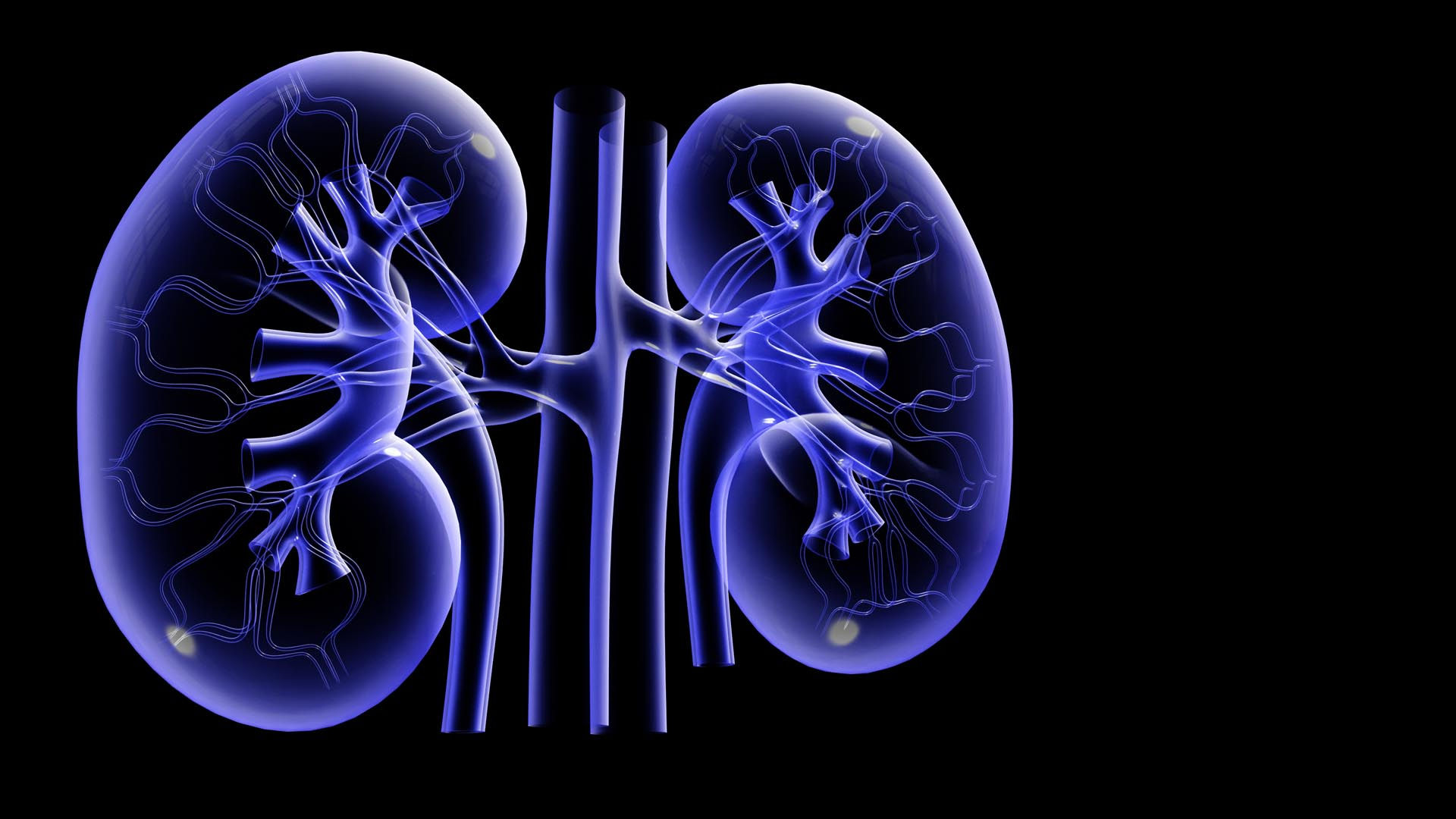

The gross anatomical structures of renal system, which include the Kidneys, Renal artery and vein, Ureter, urinary bladder, urethra and the basic structures inside the kidney. Overview, description and functions of the nephrons, biochemical changes, diffusion gradients across the various parts in the kidney leading to the formation of urine,composition and chemical properties of urine and pathophysiology.
Physiology of Kidney
Chronic Kidney Disease

Chronic Kidney disease abbreviated as CKD is the gradual loss of kidney function over the period of time. There are stages to CKD, where in the last stage the glomerular filtration ceases completely, causing accumulation of fluids and wastes in the body, also known as End Stage Renal disease. The pathophysiology behind CKD shall be discussed in detail, the symptoms occuring with the start of CKD, comparison of figures with respect to CKD in patients.
Research towards Cure

Chronic kidney disease often, cannot be cured completely, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are the treatments which support the people suffering from CKD. Some drugs and treatments slow the external symptoms related to CKD. Kidney transplant is a cure for CKD patients, though still the patients will have to undergo drug therapy for the rest of their lives.

The effect of CKD with respect to general population, the statistics and causes.

Treatment
What kind of treatments are available? Which is the most preferred and compatible, an indepth look into hemodialysis.



